Understanding the internet

The Internet for Lawyers (reprise)
I have been writing about the internet for lawyers since 1995 when it first entered the public consciousness and the first few legal websites were born. These early writings, and many since, are published on my blog Binary Law. In 2007 I joined Delia Venables editing the Internet Newsletter for Lawyers, launching the Newsletter online […]
Read More
An internet primer: connectivity
We discussed in the first article in this series how our internet service provider (ISP) connects us to the internet. Here we look at how we connect to each other and our ISP and what other technologies are at work influencing our internet connectivity and experience. Modems and routers A modem (modulator-demodulator) converts data from […]
Read More
An internet primer: web addresses and web pages
URLs A Uniform Resource Locator (URL), colloquially termed a web address, is a reference to a web resource that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. A URL is a specific type of Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), although many people use the two terms interchangeably. The most common URLs […]
Read More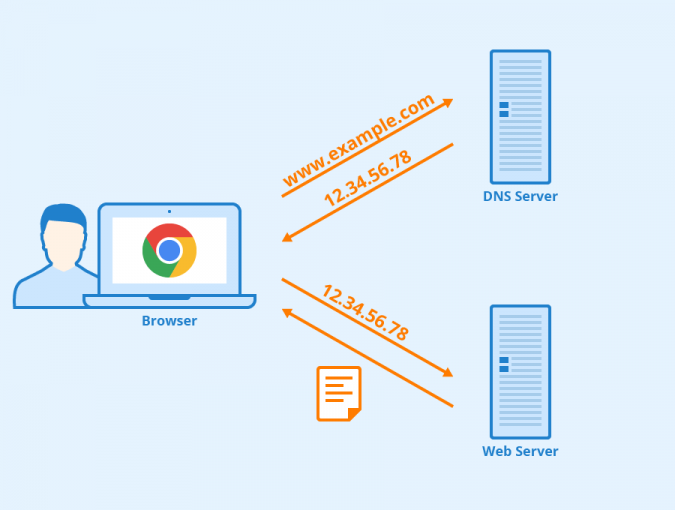
An internet primer: the Domain Name System
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical, decentralised naming system for computers, services and other resources connected to the internet. It translates domain names (like yourfirm.com) to the numerical IP addresses needed for locating and identifying computer services and devices with the underlying network protocols (like 95.232.149.44). The DNS provides a worldwide, distributed directory […]
Read More
An internet primer: what is the internet?
The Internet Newsletter for Lawyers was launched in the late 90s as there was at that time a thirst for guidance on what this new thing called the internet was and what it could offer the lawyer. Today we all take the internet for granted and few concern ourselves with what it actually is, even […]
Read More
What is encryption?
Encryption is a way of making data secure, so that it can only be accessed by authorised parties. Cryptographic techniques are used to render information unintelligible to any third parties whilst it is being stored on an electronic device such as a laptop or smartphone, or during its transit from sender to recipient over the […]
Read More
What are smart contracts?
The origin of the term “smart contract” has been attributed to Nick Szabo who wrote a paper in the late 90s in which he described them as combining “protocols with user interfaces to formalize and secure relationships over computer networks.” However, the more popular meaning of “smart contract” in current parlance, and for purposes of […]
Read More
What is predictive coding?
Predictive coding is a form of technology assisted review (TAR) used to assess the relevance of high volumes of documents for purposes of electronic disclosure (e-disclosure). E-disclosure refers to the disclosure of all electronically stored information (ESI) – as opposed to any hard copy documents – as part of the litigation process. How does it […]
Read More
What is Net Neutrality?
Net neutrality is the idea that all data sent across the internet should be treated equally, without the application of any discriminatory filtering based on specific criteria. To better understand the concept, it helps to view the internet as a “dumb” network of pipes merely facilitating the flow of data from one location (eg a […]
Read More
What is the blockchain?
A blockchain is literally a chain of blocks of data recording transactions, connected using digital, cryptographic signatures. Confusingly, blockchain technology is often referred to simply as “Blockchain” (with cap B) or as “the blockchain” (with the definite article prepended). No doubt this usage stems from its initially unique and most widely-known application as the technology […]
Read More
Big Data: an introduction
The term “big data” essentially refers to very large sets of data, as well as the processes used for capturing, analysing and extracting value from these data sets. An often-quoted definition of big data is Gartner’s 3 Vs: “Big data is high-volume, high-velocity and/or high-variety information assets that demand cost-effective, innovative forms of information processing […]
Read More
Open access explained
Open access (OA), in its simplest form, means unrestricted online access to research outputs. These outputs cover all forms of research including journal articles, conference papers, book chapters, monographs and more. In its wider sense any kind of digital content can be open access, from texts and data to software, audio, video and multi-media. But what do […]
Read More